Imagine if every time you wanted to pay for groceries, the cashier had to process every single transaction made that day before yours could go through. That’s the problem blockchains have been facing—until now. Sharding in Blockchain is being hailed as a game-changer for speeding up and scaling blockchain systems. And as artificial intelligence (AI) grows more powerful and data-hungry, sharding could be the foundation that supports this new digital future.
Let’s break down what sharding is, why it matters, and how it connects with AI in a way that’s easy to understand.
What Is Sharding in Blockchain? (And Why You Should Care)
The Basic Idea
In simple terms, sharding is a way to split a database into smaller parts called “shards.” These shards can work independently, which makes the whole system faster and more efficient.
Think of a blockchain like a big, slow train carrying lots of cargo (transactions). With sharding, instead of one train, you have many smaller, faster trains. Each train carries only part of the cargo, and they all move at the same time.
Why Blockchains Are Slow (Without Sharding)
Most blockchains, like Bitcoin and early versions of Ethereum, require every node (computer in the network) to process every transaction. This is great for security but terrible for speed and scalability.
How Sharding Changes the Game
With sharding:
- Each node only processes a part of the total data.
- Transactions can be handled in parallel.
- The system doesn’t get bogged down as more users join.
This makes it possible to scale blockchain technology to support global financial systems, supply chains, and AI applications.
Historical Context: Where Did Sharding Come From?
Sharding isn’t new. It’s been used in traditional databases for decades. For example, big companies like Google and Amazon use sharding to handle billions of user requests every day.
The real innovation is applying sharding to blockchains—decentralized systems that need to be both secure and efficient.
Ethereum 2.0 is one of the most talked-about blockchain projects adopting sharding to solve its scalability problems.
How Sharding Works in Blockchain Systems
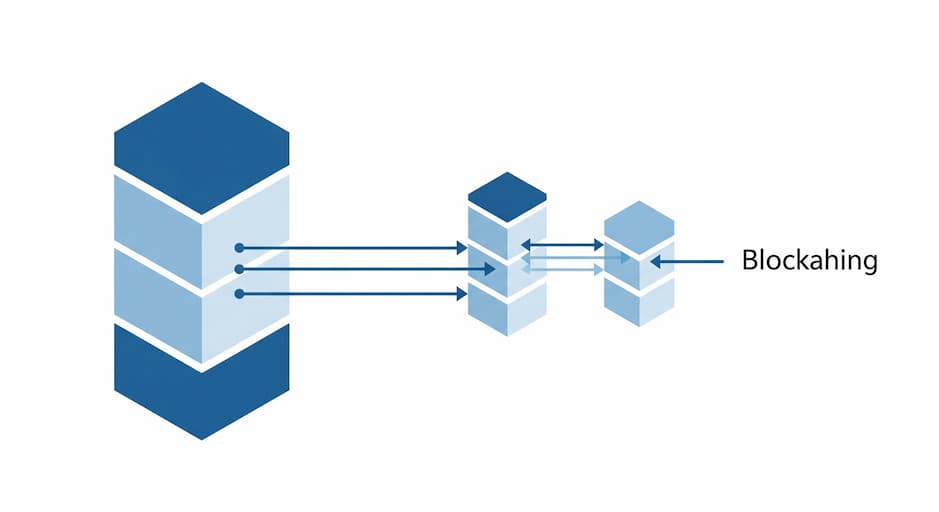
1. The Blockchain Is Divided into Shards
Each shard handles its own transactions and smart contracts. Think of them as mini-blockchains within the bigger chain.
2. Coordinators Keep Everything in Sync
There’s a central system (often called the “beacon chain” in Ethereum 2.0) that keeps track of what’s happening in each shard.
3. Cross-Shard Communication
The shards can talk to each other, so you can still move money or data from one shard to another.
4. Security Measures
Special protocols make sure that no shard gets hacked or compromised, even though not every node sees every transaction.
Why Sharding Is Crucial for AI Integration
AI Needs Massive Data and Speed
AI systems, especially those used in healthcare, finance, and logistics, process vast amounts of data. Traditional blockchains can’t keep up with the volume or speed required.
Sharding allows AI to:
- Access and store data more quickly
- Work with decentralized systems without slowdowns
- Ensure data security and integrity across global networks
Example: Healthcare Records
Imagine an AI model diagnosing diseases using data from hospitals across the world. With a sharded blockchain, each hospital can manage its own data shard, while the AI system pulls needed information in real time—securely and efficiently.
Example: Smart Cities
In smart cities, AI manages traffic, energy use, and public safety. Sharded blockchain systems could help by processing data from different city sectors in parallel.
Benefits of Sharding in Blockchain
- Scalability: Supports thousands of transactions per second.
- Efficiency: Reduces load on individual nodes.
- Cost-Effective: Lower energy and hardware needs.
- Security: With the right protocols, remains secure even with distributed processing.
Challenges and Risks
Complexity
Sharded systems are harder to design and maintain. There’s more room for bugs and security issues.
Cross-Shard Communication
Ensuring smooth, secure communication between shards is still a work in progress in many projects.
Centralization Risks
If not carefully managed, sharding could lead to some shards becoming more powerful than others.
Real-World Use Cases and Projects
Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum is moving toward a sharded architecture to handle more users and reduce fees.
Zilliqa
A blockchain project that already uses sharding to increase throughput.
NEAR Protocol
NEAR uses a unique type of sharding called “Nightshade” to manage growing user demand.
The Future of Sharding and AI
As both blockchain and AI evolve, we’ll likely see:
- More collaboration between AI and decentralized systems
- Smarter, real-time decision-making based on secure, distributed data
- Governments and companies adopting sharded systems for public infrastructure
Final Thoughts: A Smarter, Faster Future
Sharding in blockchain may sound technical, but it’s really about making systems work better for all of us. From faster payments to smarter healthcare and more responsive AI, sharding could be the foundation of our digital future.
As always, the technology is only as good as how we use it. If designed and implemented with care, sharding could unlock new possibilities that benefit everyone—from coders and entrepreneurs to teachers and shopkeepers.
What do you think? Would you trust a decentralized AI system to manage your healthcare or finances?
References
- Ethereum Foundation: https://ethereum.org/en/upgrades/sharding/
- Zilliqa Whitepaper: https://docs.zilliqa.com/whitepaper.pdf
- NEAR Protocol Docs: https://docs.near.org/
- IBM on AI and Blockchain: https://www.ibm.com/blogs/blockchain/ai-blockchain/
- CoinDesk Articles on Blockchain Scaling: https://www.coindesk.com